Politics
James Watson, co-discoverer of the double-helix shape of DNA, has died at age 97 – National TenX News
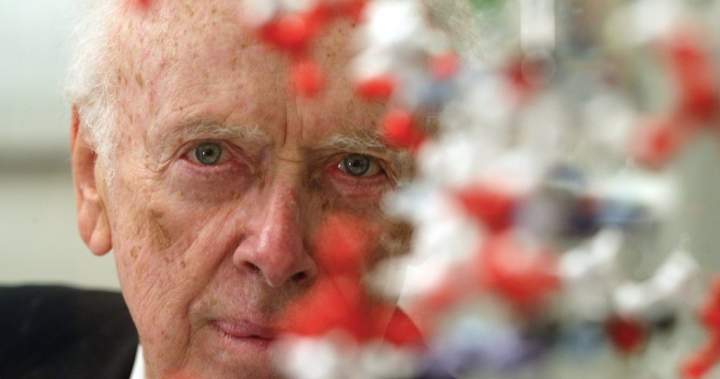
James D. Watson, whose co-discovery of the twisted-ladder structure of DNA in 1953 helped light the long fuse on a revolution in medicine, crimefighting, genealogy and ethics, has died. He was 97.
The breakthrough — made when the brash, Chicago-born Watson was just 24 — turned him into a hallowed figure in the world of science for decades. But near the end of his life, he faced condemnation and professional censure for offensive remarks, including saying Black people are less intelligent than white people.
Watson shared a 1962 Nobel Prize with Francis Crick and Maurice Wilkins for discovering that deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is a double helix, consisting of two strands that coil around each other to create what resembles a long, gently twisting ladder.
That realization was a breakthrough. It instantly suggested how hereditary information is stored and how cells duplicate their DNA when they divide. The duplication begins with the two strands of DNA pulling apart like a zipper.
Even among non-scientists, the double helix would become an instantly recognized symbol of science, showing up in such places as the work of Salvador Dali and a British postage stamp.
The discovery helped open the door to more recent developments such as tinkering with the genetic makeup of living things, treating disease by inserting genes into patients, identifying human remains and criminal suspects from DNA samples and tracing family trees. But it has also raised a host of ethical questions, such as whether we should be altering the body’s blueprint for cosmetic reasons or in a way that is transmitted to a person’s offspring.
“Francis Crick and I made the discovery of the century, that was pretty clear,” Watson once said. He later wrote: “There was no way we could have foreseen the explosive impact of the double helix on science and society.”
Watson never made another lab finding that big. But in the decades that followed, he wrote influential textbooks and a best-selling memoir and helped guide the project to map the human genome. He picked out bright young scientists and helped them. And he used his prestige and contacts to influence science policy.
Watson died in hospice care after a brief illness, his son said Friday. His former research lab confirmed he passed away a day earlier.
“He never stopped fighting for people who were suffering from disease,” Duncan Watson said of his father.
Watson’s initial motivation for supporting the gene project was personal: His son Rufus had been hospitalized with a possible diagnosis of schizophrenia, and Watson figured that knowing the complete makeup of DNA would be crucial for understanding that disease — maybe in time to help his son.
He gained unwelcome attention in 2007, when the Sunday Times Magazine of London quoted him as saying he was “inherently gloomy about the prospect of Africa” because “all our social policies are based on the fact that their intelligence is the same as ours — where all the testing says not really.” He said that while he hopes everyone is equal, “people who have to deal with black employees find this is not true.”
Related Videos
He apologized, but after an international furor he was suspended from his job as chancellor of the prestigious Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory in New York. He retired a week later. He had served in various leadership jobs there for nearly 40 years.
In a television documentary that aired in early 2019, Watson was asked if his views had changed. “No, not at all,” he said. In response, the Cold Spring Harbor lab revoked several honorary titles it had given Watson, saying his statements were “reprehensible” and “unsupported by science.”

Get weekly health news
Receive the latest medical news and health information delivered to you every Sunday.
Watson’s combination of scientific achievement and controversial remarks created a complicated legacy.
He has shown “a regrettable tendency toward inflammatory and offensive remarks, especially late in his career,” Dr. Francis Collins, director of the National Institutes of Health, said in 2019. “His outbursts, particularly when they reflected on race, were both profoundly misguided and deeply hurtful. I only wish that Jim’s views on society and humanity could have matched his brilliant scientific insights.”
Long before that, Watson scorned political correctness.
“A goodly number of scientists are not only narrow-minded and dull, but also just stupid,” he wrote in “The Double Helix,” his bestselling 1968 book about the DNA discovery.
For success in science, he wrote: “You have to avoid dumb people. … Never do anything that bores you. … If you can’t stand to be with your real peers (including scientific competitors) get out of science. … To make a huge success, a scientist has to be prepared to get into deep trouble.”
It was in the fall of 1951 that the tall, skinny Watson — already the holder of a Ph.D. at 23 — arrived at Britain’s Cambridge University, where he met Crick. As a Watson biographer later said, “It was intellectual love at first sight.”
Crick himself wrote that the partnership thrived in part because the two men shared “a certain youthful arrogance, a ruthlessness, and an impatience with sloppy thinking.”
Together they sought to tackle the structure of DNA, aided by X-ray research by colleague Rosalind Franklin and her graduate student Raymond Gosling. Watson was later criticized for a disparaging portrayal of Franklin in “The Double Helix,” and today she is considered a prominent example of a female scientist whose contributions were overlooked. (She died in 1958.)
Watson and Crick built Tinker Toy-like models to work out the molecule’s structure. One Saturday morning in 1953, after fiddling with bits of cardboard he had carefully cut to represent fragments of the DNA molecule, Watson suddenly realized how these pieces could form the “rungs” of a double helix ladder.
His first reaction: “It’s so beautiful.”
Following the discovery, Watson spent two years at the California Institute of Technology, then joined the faculty at Harvard in 1955. Before leaving Harvard in 1976, he essentially created the university’s program for molecular biology, scientist Mark Ptashne recalled in a 1999 interview.
Watson became director of the Cold Spring Harbor lab in 1968, its president in 1994 and its chancellor 10 years later. He made the lab on Long Island an educational center for scientists and non-scientists, focused research on cancer, instilled a sense of excitement and raised huge amounts of money.
He transformed the lab into a “vibrant, incredibly important center,” Ptashne said. It was “one of the miracles of Jim: a more disheveled, less smooth, less typically ingratiating person you could hardly imagine.”
From 1988 to 1992, Watson directed the federal effort to identify the detailed makeup of human DNA. He created the project’s huge investment in ethics research by simply announcing it at a news conference. He later said it was “probably the wisest thing I’ve done over the past decade.”
Watson was on hand at the White House in 2000 for the announcement that the federal project had completed an important goal: a “working draft” of the human genome, basically a road map to an estimated 90 percent of human genes.
Researchers presented Watson with the detailed description of his own genome in 2007. It was one of the first genomes of an individual to be deciphered.
Watson knew that genetic research could produce findings that make some people uncomfortable. In 2007, he wrote that when scientists identify genetic variants that predispose people to crime or significantly affect intelligence, the findings should be publicized rather than squelched out of political correctness.
James Dewey Watson was born in Chicago on April 6, 1928, into “a family that believed in books, birds and the Democratic Party,” as he put it. From his birdwatcher father he inherited an interest in ornithology and a distaste for explanations that didn’t rely on reason or science.
Watson was a precocious child who loved to read, studying books like “The World Telegraph Almanac of Facts.” He entered the University of Chicago on a scholarship at 15, graduated at 19 and earned his doctorate in zoology at Indiana University three years later.
He got interested in genetics at age 17 when he read a book that said genes were the essence of life.
“I thought, ‘Well, if the gene is the essence of life, I want to know more about it,’” he later recalled. “And that was fateful because, otherwise, I would have spent my life studying birds and no one would have heard of me.”
At the time, it wasn’t clear that genes were made of DNA, at least for any life form other than bacteria. But Watson went to Europe to study the biochemistry of nucleic acids like DNA. At a conference in Italy, Watson saw an X-ray image that indicated DNA could form crystals.
“Suddenly I was excited about chemistry,” Watson wrote in “The Double Helix.” If genes could crystallize, “they must have a regular structure that could be solved in a straightforward fashion.”
“A potential key to the secret of life was impossible to push out of my mind,” he recalled.
In the decades after his discovery, Watson’s fame persisted. Apple Computer used his picture in an ad campaign. At conferences, graduate students who weren’t even born when he worked at Cambridge nudged each other and whispered, “There’s Watson. There’s Watson.” They got him to autograph napkins or copies of “The Double Helix.”
A reporter asked him 2018 if any building at the Cold Spring Harbor lab was named after him. No, Watson replied, “I don’t need a building named after me. I have the double helix.”
His 2007 remarks on race were not the first time Watson struck a nerve with his comments. In a speech in 2000, he suggested that sex drive is related to skin color. And earlier he told a newspaper that if a gene governing sexuality were found and could be detected in the womb, a woman who didn’t want to have a gay child should be allowed to have an abortion.
More than a half-century after winning the Nobel, Watson put the gold medal up for auction in 2014. The winning bid, $4.7 million, set a record for a Nobel. The medal was eventually returned to Watson.
Both of Watson’s Nobel co-winners, Crick and Wilkins, died in 2004.
___
Ritter is a retired AP science writer. AP science writers Christina Larson in Washington and Adithi Ramakrishnan in New York contributed to this report.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Politics
Louvre raises ticket prices for non-Europeans, hitting Canadian visitors TenX News

A trip to the world’s most-visited museum is about to cost Canadians significantly more.
France has hiked ticket prices at the Louvre by 45 per cent for visitors from outside the European Union, a move that is fuelling debate over so-called dual pricing and the growing backlash against overtourism.
Starting this week, adult visitors from non-EU countries, including Canada, must pay €32 to enter the Paris landmark, up from €22. That’s an increase from about $35 to $52 Canadian.

Visitors from EU countries, as well as Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, will continue to pay the lower rate.
The price hike comes as the Louvre grapples with repeated labour strikes, a high-profile daylight jewel heist last October that prompted a costly security overhaul, and years of chronic overcrowding. The museum attracts roughly nine million visitors annually.

Get breaking National news
For news impacting Canada and around the world, sign up for breaking news alerts delivered directly to you when they happen.
Some Canadian tourists told Global News they feel unfairly targeted.
“We didn’t cause the robberies or some of the other issues that happened and we are paying the consequences,” said Allison Moore, visiting Paris from Newfoundland with her daughter. “[In] Canada we don’t discriminate over pricing like that.”
Others argue tourists already shoulder higher costs simply by travelling long distances.
“In general for tourists, I think things should be a little cheaper than for local people, because we have to travel to come all the way here,” said Darla Daniela Quiroz, another Canadian visitor. “It should be equal pricing, or a little bit cheaper.”

Even some Europeans question the two-tiered system. A French tourist interviewed outside the museum said there was “no reason” to charge non-Europeans more and that the fee should be the same for everyone.
Tourism experts say the Louvre’s financial pressures help explain the decision.
“The Louvre is really cash-strapped right now and needs to do something,” said Marion Joppe, a professor at the University of Guelph. “It can’t really look to the government, which is already struggling with its own budget.”
The move also reflects a broader global pushback against mass tourism. Anti-tourism protests have spread across parts of Spain, New Zealand has increased its entry tax, and the United States recently raised national park fees for foreign visitors.
“You take Paris — it gets about 50 million tourists a year,” said Julian Karaguesian, an economist at McGill University. “That’s roughly a million a week. The city simply wasn’t built for those kinds of numbers.”
Despite the higher price, many visitors say they will still line up to see the Mona Lisa and other of the museum’s famous artworks.
“It’s one of the main attractions. It’s on everybody’s list,” Moore said. “We’re still going to go, and hopefully it will be worth it in the end.”
© 2026 Global News, a division of Corus Entertainment Inc.
Politics
Trump calls Canada-China deal ‘good thing’ as U.S. officials voice concern – National TenX News

Canada’s new trade deal with China is getting a mixed reaction in Washington, with U.S. President Donald Trump voicing support as administration officials warned Ottawa could regret allowing Chinese EVs into the Canadian market.
The deal signed with Beijing on Friday reverses course on 100 per cent tariffs Canada slapped on Chinese electric vehicles in 2024, which aligned with similar U.S. duties. Canada and China also agreed to reduce tariffs on canola and other products.
Asked about the deal by reporters at the White House, Trump said Prime Minister Mark Carney was doing the right thing.
“That’s what he should be doing. It’s a good thing for him to sign a trade deal. If you can get a deal with China, you should do that,” Trump said.
However, members of Trump’s cabinet expressed concern.
“I think they’ll look back at this decision and surely regret it to bring Chinese cars into their market,” U.S. Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy said at an event with other U.S. government officials at a Ford factory in Ohio to tout efforts to make vehicles more affordable.
U.S. Trade Representative Jamieson Greer told reporters the limited number of vehicles would not impact American car companies exporting cars to Canada.
“I don’t expect that to disrupt American supply into Canada,” he said.
“Canada is so dependent on the United States for their GDP. Their entire population is crowded around our border for that reason. I’ll tell you one thing: if those cars are coming into Canada, they’re not coming here. That’s for sure.”

Get daily National news
Get the day’s top news, political, economic, and current affairs headlines, delivered to your inbox once a day.
Carney has said it’s necessary for Canada to improve trade ties and cooperation with China in light of Trump’s trade war and threats to let the Canada-U.S.-Mexico Agreement on free trade expire.

The trade pact is up for review this summer, and Greer reiterated that the Trump administration wants to bring more auto manufacturing back to the U.S. and incentivize companies to do so.
Under the new deal with Beijing, Carney said he expects China will lower tariffs on its canola seed by March 1 to a combined rate of about 15 per cent.
Greer questioned that agreement in a separate CNBC interview.
“I think in the long run, they’re not going to like having made that deal,” he said.
He called the decision to allow Chinese EVs into Canada “problematic” and added: “There’s a reason why we don’t sell a lot of Chinese cars in the United States. It’s because we have tariffs to protect American auto workers and Americans from those vehicles.”
Greer said rules adopted last January on vehicles that are connected to the internet and navigation systems are a significant impediment to Chinese vehicles in the U.S. market.
“I think it would be hard for them to operate here,” Greer said. “There are rules and regulations in place in America about the cybersecurity of our vehicles and the systems that go into those, so I think it might be hard for the Chinese to comply with those kind of rules.”

Trump and officials like Greer have taken aim at Chinese attempts to enter the North American car market through Mexico by bypassing rules of origin under CUSMA.
The CUSMA review set for July is expected to address those loopholes that American and Canadian officials have said are being exploited by China.
Those concerns, which were also raised by the Biden administration, in part helped spur the steep tariffs on Chinese EVs, which are heavily subsidized by Beijing.
Trump, however, has also said he would like Chinese automakers to come to the United States to build vehicles.
Both Democrat and Republican lawmakers in the U.S. have expressed strong opposition to Chinese vehicles as major U.S. automakers warn China poses a threat to the U.S. auto sector.
Ohio Senator Bernie Moreno, a Republican, said at Friday’s event at the Ford plant that he was opposed to Chinese vehicles coming into the United States, and drew applause from the other government officials.
“As long as I have air in my body, there will not be Chinese vehicles sold the United States of America — period,” Moreno said.
—with files from Reuters
© 2026 Global News, a division of Corus Entertainment Inc.
Politics
Canada-China trade deal framed as a win for B.C.’s economy TenX News

Prime Minister Mark Carney’s trade mission to China is being framed as a win for British Columbia’s economy.
Carney announced a new deal with Beijing on electric vehicles and canola at the end of a high-profile trip on Friday.
“The inroads Canada has made this week are a sign that the government gets it and is showing Canadians and the world that we are open for business,” Alexa Young with the Vancouver Fraser Port Authority said.
The trade deal would allow up to 49,000 Chinese EVs into Canada yearly at a tariff rate of 6.1 per cent.
An expanded auto terminal on Annacis Island will be able to handle the additional volume of cars that could be more affordable than what is currently on the market, with prices expected to be under $40,000.
The New Car Dealers Association said in a statement to Global News that, “We look forward to reviewing the full details of this announcement and engaging constructively with governments to ensure that affordability, competition, and long-term market stability remain central considerations.”

In British Columbia, the overall reaction to the news on Friday is positive.

Get breaking National news
For news impacting Canada and around the world, sign up for breaking news alerts delivered directly to you when they happen.
“China’s economy is important,” Alex McMillan with the B.C. Chamber of Commerce said.
“Having trade deals like this — and diversifying our markets — is important. Providing certainty is important.”
There are concerns with the agreement, including privacy issues and China’s human rights record. But Ottawa’s goal is to double trade with partners outside the United States, which is a goal that would be impossible without China.
“We do want to see more trade and more diversification of our markets and know that China is an important nation and important economy, so having better trade relationships with them, I think overall is going to be good,” McMillan said.
–with files from The Canadian Press
© 2026 Global News, a division of Corus Entertainment Inc.
-

 Fashion10 months ago
Fashion10 months agoThese ’90s fashion trends are making a comeback in 2017
-

 Entertainment10 months ago
Entertainment10 months agoThe final 6 ‘Game of Thrones’ episodes might feel like a full season
-

 TenX Exclusive10 months ago
TenX Exclusive10 months agoअमर योद्धा: राइफलमैन जसवंत सिंह रावत की वीरगाथा
-

 Politics8 months ago
Politics8 months agoBefore being named Pope Leo XIV, he was Cardinal Robert Prevost. Who is he? – National TenX News
-

 Politics9 months ago
Politics9 months agoPuerto Rico faces island-wide blackout, sparking anger from officials – National TenX News
-

 Fashion10 months ago
Fashion10 months agoAccording to Dior Couture, this taboo fashion accessory is back
-

 Tech10 months ago
Tech10 months agoIndian-AI-software-which-caught-30-thousand-criminals-and-busted-18-terrorist-modules-its-demand-is-increasing-in-foreign-countries-also – News18 हिंदी
-

 Politics9 months ago
Politics9 months agoScientists detect possible signs of life on another planet — but it’s not aliens – National TenX News















